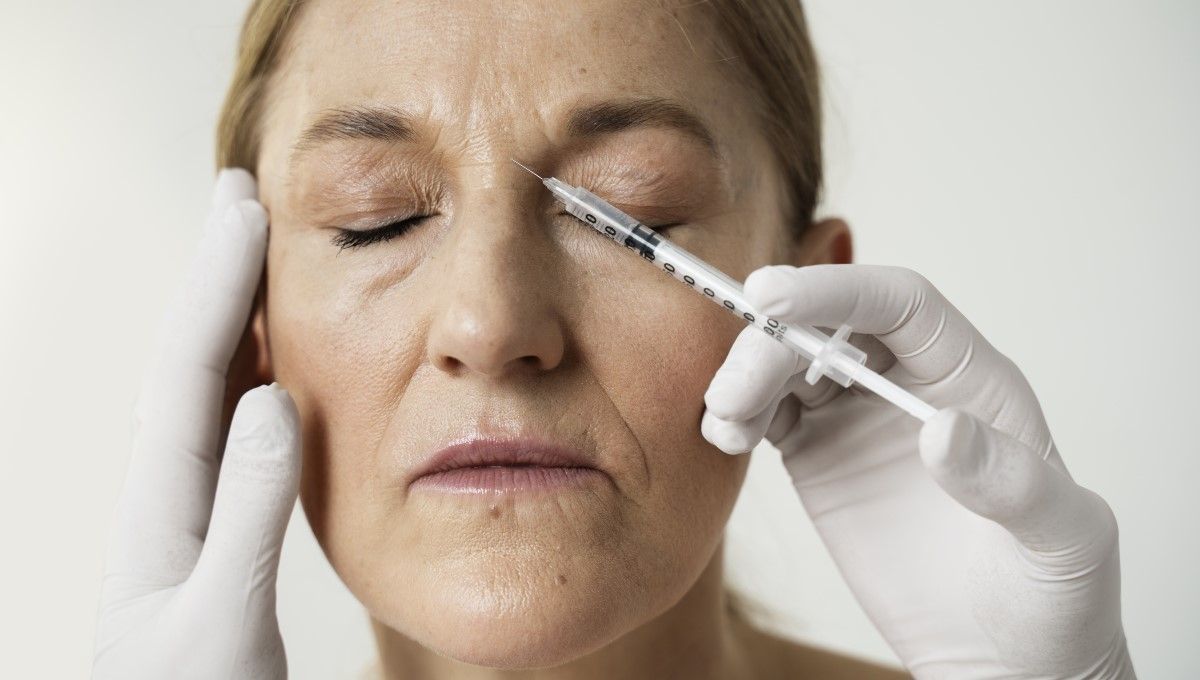
The evolution of aesthetic medicine does not stop, and new disciplines, as well as trends in procedures, are becoming increasingly more effective and innovative. as mentioned Dr. Mar Meira and Sofia Ruiz del CuetoResearch continues on neuromodulators aimed at ensuring that patients can enjoy Very fast and long lasting resultsThe quality of the process is still intact.
Although medical approval is a long process He can be dull.
latest treatments
Doctors explain which are two new substances that promise to quickly and permanently eliminate dynamic wrinkles over time. they are about Type E Neuromodulators and Fastox, Experts also comment on the treatment that is pending approval and which will represent an innovation in aesthetic medicine: Infiltration with neuromodulators into the platysma muscle.
type e neuromodulator, in aesthetic medicine Type A neuromodulators currently in useAlthough type E is known, it has not been used clinically. Its uses include beautifying facial aging quickly. Since the beginning of its action, appears within a few hours And it is considered a “flash effect” neuromodulator.
fastox, It is a combination of muscle relaxants, Although it is not a neuromodulator, its purpose is to add infiltration with neuromodulator extend period Action on dynamic wrinkles. A study conducted by the Swiss biotechnology company Fastox, created by experts in biotechnology and neuromodulators.
Neuromodulator in platysma muscle, Application of neuromodulators in platysma muscle It is also being evaluated, currently it is in the process of approval. Its purpose is to treat wrinkles that form in the area neck,
Through small infiltrates appearing as papuleswhere the largest number is contractionHe marks the oval of the face avoid the formation of “Platysmal Band”, The first presentation of this process is from here 4-5 days after treatmentWith a lasting effect of up to 6 months,